Anti Earthquake Technology In Japanese Homes
Japan is a global leader in anti-earthquake (seismic) technology, especially in residential construction. Here’s a clear overview of the key technologies and strategies used in Japanese homes to protect against earthquakes:
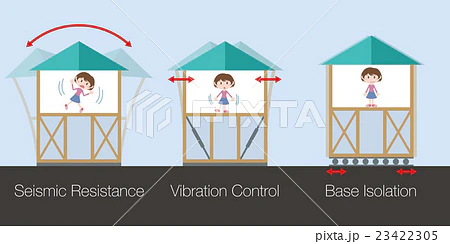
🏠 1. Seismic Isolation (免震 – Menshin)

How it works:
The house is built on base isolators (usually rubber bearings with metal plates) that absorb seismic waves, reducing the shaking transferred to the building.
Common in: High-end homes and mid-rise apartment buildings.
Benefits:
- Minimizes interior damage.
- Keeps furniture and appliances stable during quakes.
Downsides:
- Higher cost (but decreasing).
- Requires space beneath the structure for installation.
🏗️ 2.Vibration Control (制震 – Seishin)

How it works:
Uses dampers (shock absorbers) inside walls, ceilings, or between floors to dissipate seismic energy.
Types of dampers:
- Oil dampers
- Steel braces
- Viscoelastic materials
Benefits:
- Less expensive than full isolation.
- Can be added to both new and existing homes.
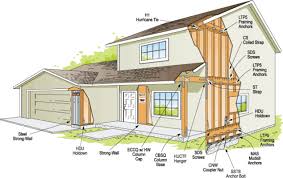
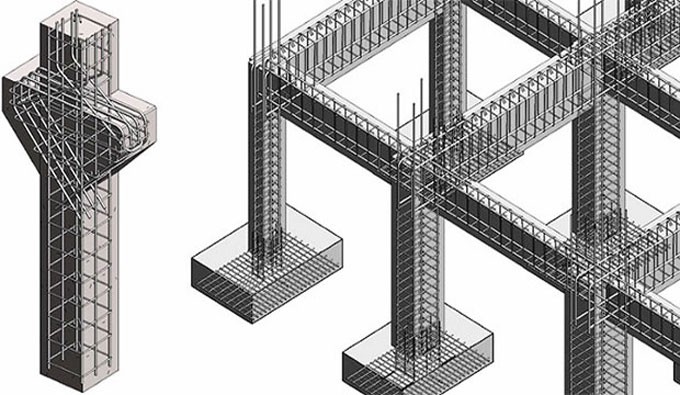
🧱 3. Reinforced Structural Design (耐震 – Taishin)
How it works:
- Homes are built to resist shaking through strong frames, shear walls, cross-bracing, and anchor bolts that tie the home to its foundation.
Materials used:
- Reinforced concrete
- Engineered wood
- Steel frames in multi-family homes
Design principles:
- Symmetry and simplicity in layout
- Load path continuity
- Lightweight roofing and materials to reduce top-heavy sway
🛠️ 4. Retrofitting Older Homes

For homes built pre-1981 (before the major code revision):
- Adding steel reinforcement
- Installing wall bracing
- Strengthening foundations
- Adding anchoring systems between roofs, walls, and floors
Government support:
- Subsidies and tax incentives are available for seismic retrofits.
🔧 5. Smart Earthquake-Response Systems
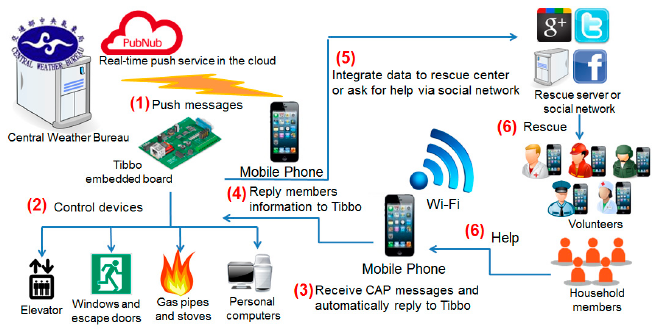
Recent additions include:
- Automatic gas shutoff valves
- Seismic alarms and early warning integration
- Smart home integration for safety systems (lights, door locks, etc.)
🌍 Example: “Earthquake-Resistant Wooden Homes”
Japan has perfected traditional wood construction by combining it with modern tech:
- Kumiki joinery (interlocking wooden joints) for flexibility
- Hidden steel rods or brackets inside the wood structure
- Use of plywood shear walls to resist lateral movement