Post-Heart Attack Diet
Experiencing a heart attack is a life-altering event that necessitates significant lifestyle changes, particularly in dietary habits. Adopting a heart-healthy diet is crucial for recovery and for reducing the risk of future cardiac events. Such a diet focuses on nutrient-rich foods that support cardiovascular health, manage blood pressure, and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. Wikipedia
A heart-healthy diet typically includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It emphasizes the reduction of saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. By making informed food choices, individuals can significantly improve their heart health and overall well-being.
Key Components of a Post-Heart Attack Diet
Emphasizing Fruits and Vegetables
Incorporating a wide range of fruits and vegetables into your daily meals provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health. Leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in nitrates, which can help lower blood pressure. Berries, such as strawberries and blueberries, contain anthocyanins that reduce inflammation and oxidative stress .The Times of India
Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal. This not only ensures a high intake of beneficial nutrients but also helps in maintaining a healthy weight, which is vital for heart health.Mayo Clinic+7Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada+7Healthline+7
Choosing Whole Grains
Whole grains like oats, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are excellent sources of fiber, which can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels. Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain all parts of the grain kernel, providing more nutrients and promoting better heart health .
Incorporate whole grains into your diet by choosing whole grain versions of bread, pasta, and cereals. Start your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fresh fruits for a heart-healthy breakfast.
Incorporating Lean Proteins
Opt for lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, legumes, and low-fat dairy products. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease .
Plant-based proteins, including beans, lentils, and tofu, are also excellent choices. They are low in saturated fat and high in fiber, making them beneficial for heart health.
Limiting Unhealthy Fats and Sodium
Reducing the intake of saturated and trans fats is essential for heart health. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Instead, focus on consuming healthy fats found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil .
Sodium can contribute to high blood pressure, a risk factor for heart disease. Limit sodium intake by avoiding processed foods, reading nutrition labels, and choosing low-sodium alternatives.
Recommended Dietary Patterns
The Mediterranean Diet

The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and healthy fats, particularly olive oil. It includes moderate amounts of fish and poultry and limits red meat and sweets. This dietary pattern has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and is recommended for individuals recovering from a heart attack .
The DASH Diet
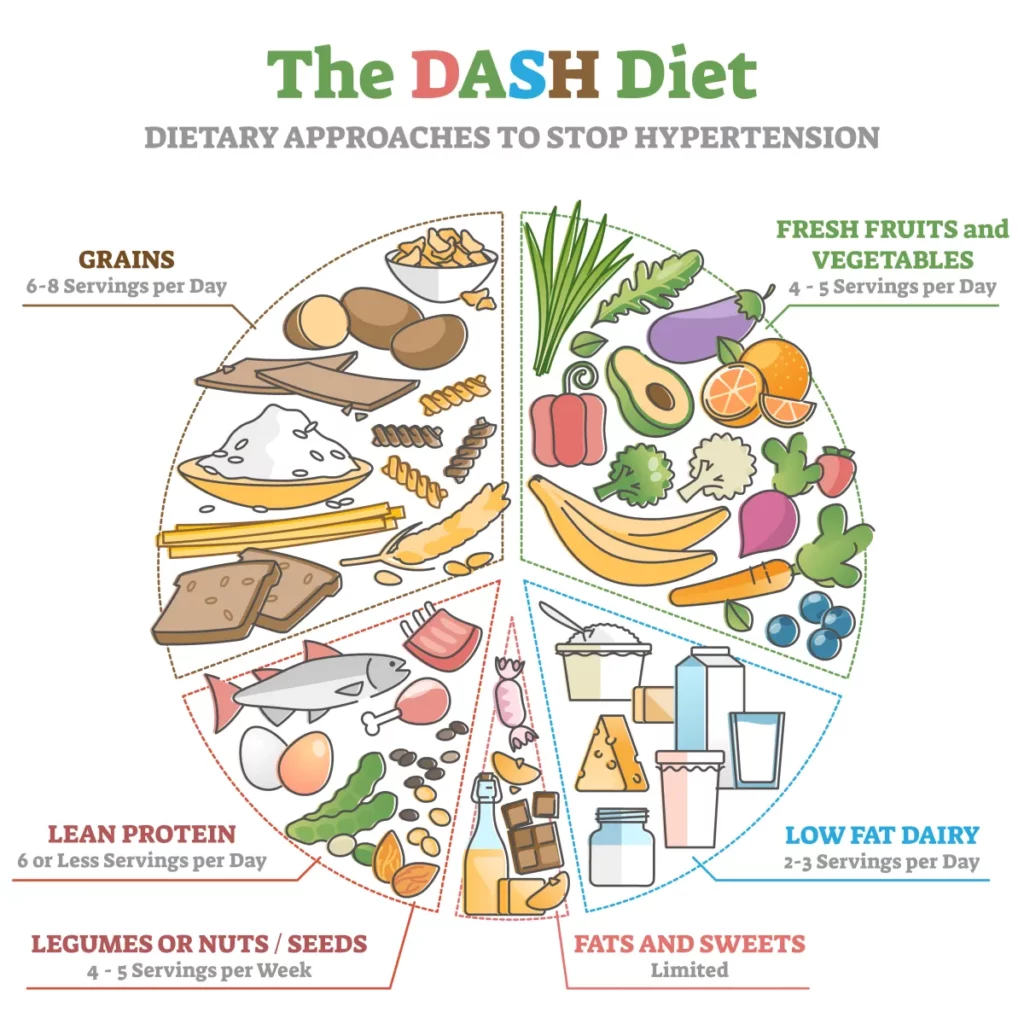
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet focuses on reducing sodium intake and increasing the consumption of nutrient-rich foods. It encourages the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. The DASH diet has been shown to lower blood pressure and improve heart health .NHLBI, NIHWikipedia
Meal Planning Tips
Creating a meal plan can help ensure a balanced and heart-healthy diet. Start by planning meals that include a variety of food groups, focusing on nutrient-dense options. Prepare meals at home to have better control over ingredients and portion sizes.
Incorporate snacks that are low in saturated fat and sodium, such as fresh fruits, unsalted nuts, or low-fat yogurt. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary beverages.
Lifestyle Considerations
In addition to dietary changes, adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for heart health. Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your heart health and make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle.