Passive house Design
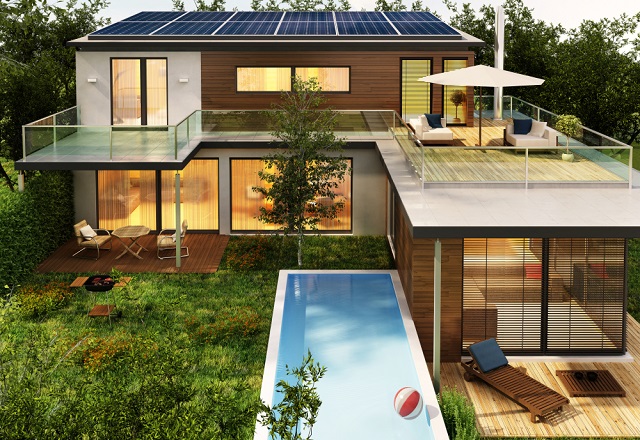
Passive house design (or Passivhaus) is a rigorous, energy-efficient building standard developed to drastically reduce a building’s energy needs for heating and cooling, while maintaining exceptional indoor comfort.
Here’s a clear breakdown of what passive house design is, its key principles, benefits, and design strategies:
🏡 What Is Passive House Design?
A Passive House is a building that uses minimal energy for heating and cooling — typically up to 90% less than conventional buildings — by leveraging smart architectural design, superior insulation, airtightness, and heat recovery ventilation.
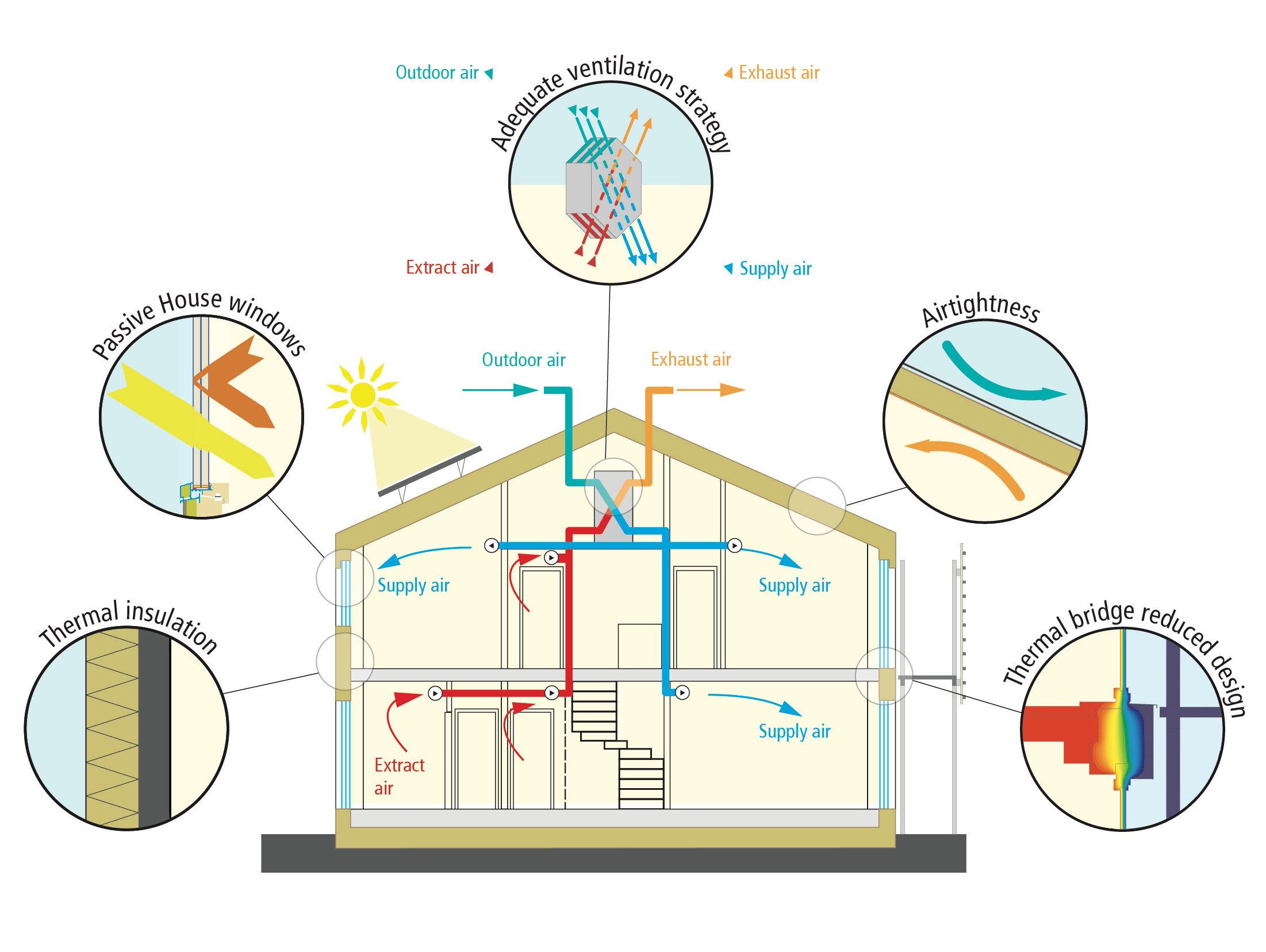
🧱 5 Core Principles of Passive House Design
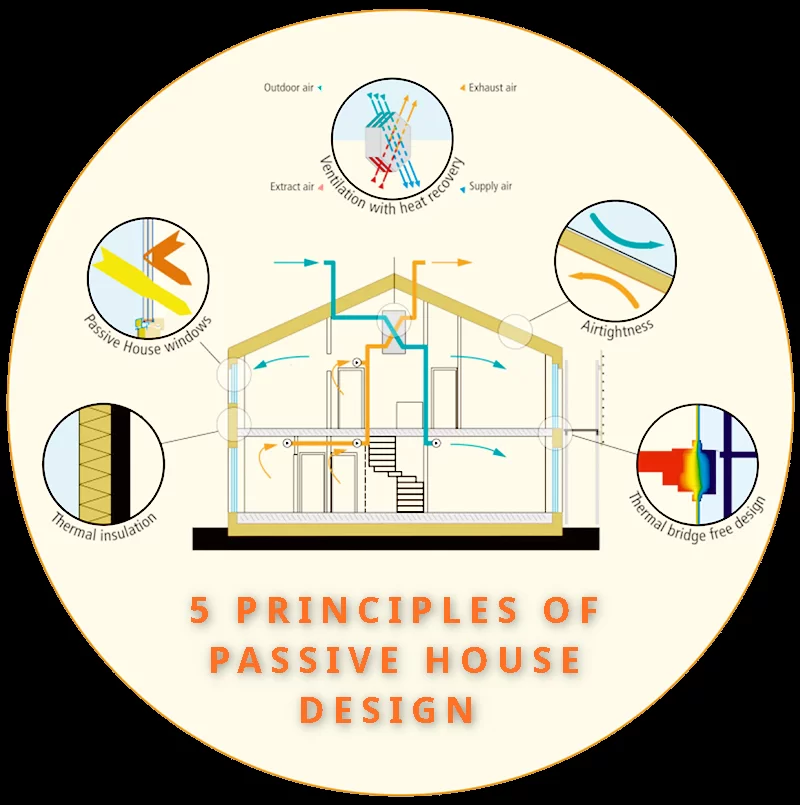
- Superinsulation
- High-performance insulation in walls, roofs, and floors minimizes heat loss.
- Typically ≥ R-40 in walls, R-60 in roofs (varies by climate).
- Airtight Building Envelope
- Extremely low air leakage to prevent heat loss and drafts.
- Measured by blower door test: ≤ 0.6 air changes per hour at 50 Pascals.
- High-Performance Windows & Doors
- Triple-glazed, low-emissivity (Low-E) windows with insulated frames.
- Orientation and shading considered for solar gain and protection.
- Thermal Bridge-Free Construction
- Eliminates heat flow paths (thermal bridges) through structural elements.
- Prevents cold spots and condensation.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) or Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV)
- Supplies constant fresh air while recovering heat from outgoing air.
- Provides superior indoor air quality without energy waste.
☀️ Design Strategies
- South-Facing Orientation (Northern Hemisphere): Maximizes passive solar heating.
- Shading Devices: Overhangs, louvers, and deciduous trees prevent overheating in summer.
- Compact Building Shape: Reduces surface area and heat loss.
- Thermal Mass: Materials like concrete or brick absorb and release heat slowly.
- Smart Zoning: Separating heated zones from unheated areas like garages or basements.
🌿 Benefits of Passive House Design
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| 💡 Ultra-Energy Efficient | Reduces heating/cooling needs by up to 90% |
| 🌡️ Consistent Comfort | No drafts or cold spots, stable temperature year-round |
| 💨 Healthy Air | Continuous filtered fresh air via ventilation system |
| 🔇 Quiet | Thick walls and triple glazing block outside noise |
| 🌍 Eco-Friendly | Significantly lower carbon footprint |
| 💰 Long-Term Savings | Lower energy bills and maintenance costs |
🛠️ Passive House Certification
- Developed by the Passive House Institute (PHI) in Germany.
- Buildings are certified based on performance metrics (energy demand, airtightness, etc.).
- Now adapted globally for different climates (e.g., cold, humid, tropical).
✅ Ideal For:
- Residential homes
- Apartment buildings
- Schools & public buildings
- Net-zero energy homes