Net Zero Energy Homes
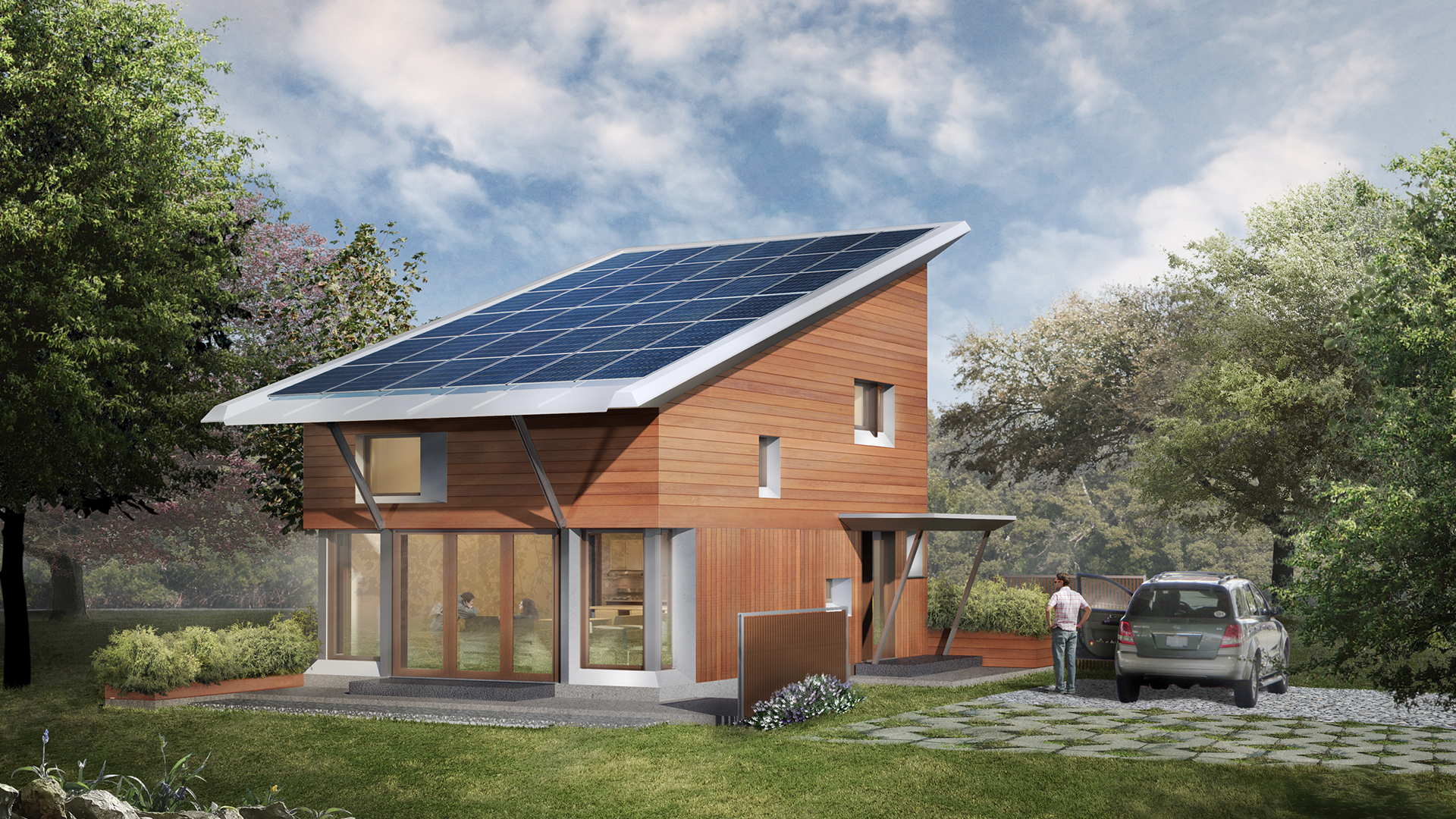
Net Zero Energy Homes (NZEH) are designed to produce as much energy as they consume on an annual basis—often using renewable energy sources like solar power. The goal is to eliminate reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon emissions, while creating an efficient, self-sustaining living environment.
🌍 What Is a Net Zero Energy Home?

A Net Zero Energy Home is a house that:
- Uses minimal energy through efficient design and technology.
- Generates renewable energy (e.g., solar panels) to match or exceed its consumption.
- Maintains high comfort, health, and performance standards.
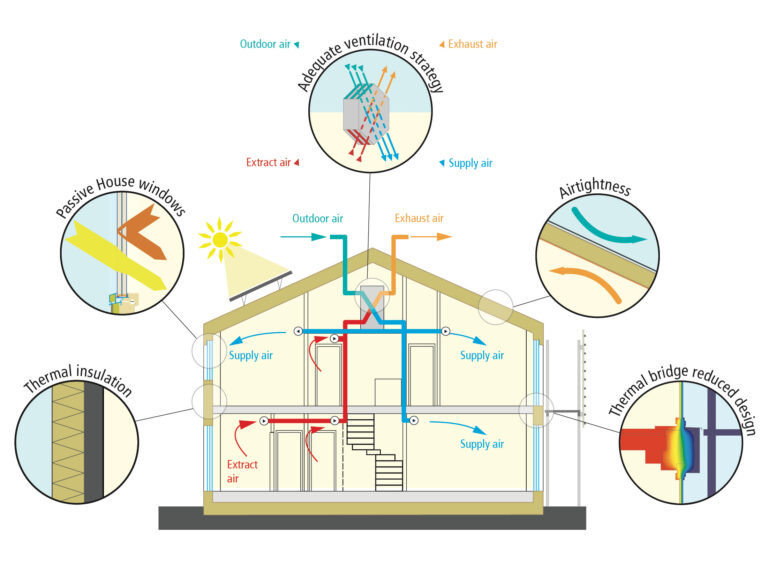
⚙️ Key Features of Net Zero Homes
1. Energy-Efficient Design
- High R-value insulation (walls, roofs, floors)
- Airtight envelope to reduce leaks
- Triple-glazed windows with low-E coatings
- Thermal bridge elimination
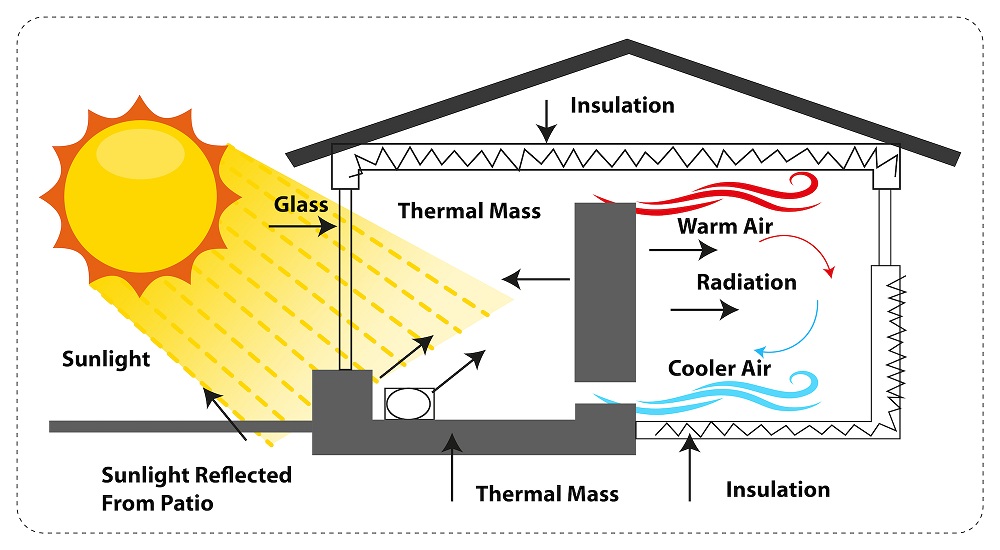
- Passive solar design (strategic orientation and window placement)
2. High-Performance HVAC Systems

- Energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs)
- Ground-source or air-source heat pumps
- Smart thermostats
3. Efficient Appliances and Lighting

- ENERGY STAR-rated appliances
- LED lighting and smart lighting systems
- Low-energy water heaters (e.g., heat pump water heaters)
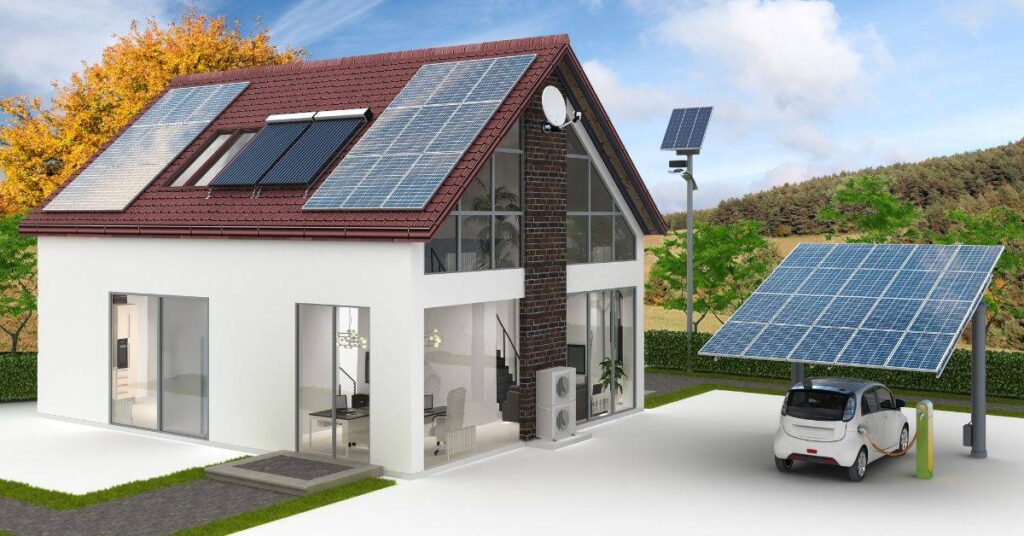
4. On-Site Renewable Energy

- Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels for electricity generation
- Optional: solar thermal systems for hot water
- Battery storage systems (e.g., Tesla Powerwall) for energy resilience
5. Smart Energy Management

- Home energy monitoring systems
- Automated systems to optimize heating, cooling, lighting, and usage patterns
🔋 Net Zero vs Passive House
| Feature | Net Zero Energy Home | Passive House |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Balance energy use with renewable production | Minimize energy demand |
| Solar Required | Yes | Not necessarily |
| Certification Body | Varies (e.g., DOE Zero Energy Ready, LEED) | Passive House Institute |
| Approach | Offset energy after use | Avoid energy use in the first place |
💡 Benefits of Net Zero Energy Homes
- $0 Energy Bills: Over a year, the energy produced equals the energy used.
- Resilience: Homes can continue functioning during power outages with battery backup.
- Sustainability: Dramatic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Health & Comfort: Better indoor air quality, quieter spaces, and thermal consistency.
- Increased Property Value: Buyers are increasingly seeking energy-efficient homes.
💰 Is It Expensive?
- Upfront Costs: ~5–15% higher than conventional builds (varies by region)
- Return on Investment:
- Lower energy bills over time
- Tax credits & incentives (e.g., solar rebates)
- Higher resale value
🛠 Example Technologies Used
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
| Solar Energy | LG NeON Solar Panels, Tesla Powerwall |
| HVAC | Mitsubishi Heat Pumps, Zehnder HRV |
| Insulation | Rockwool, cellulose, spray foam |
| Smart Controls | Google Nest, Sense Energy Monitor |
| Windows | Alpen triple-pane, Marvin Elevate |