Lidar and Radar in Autonomous Vehicles
Lidar and Radar in Autonomous Vehicles: A Comprehensive Comparison
Introduction
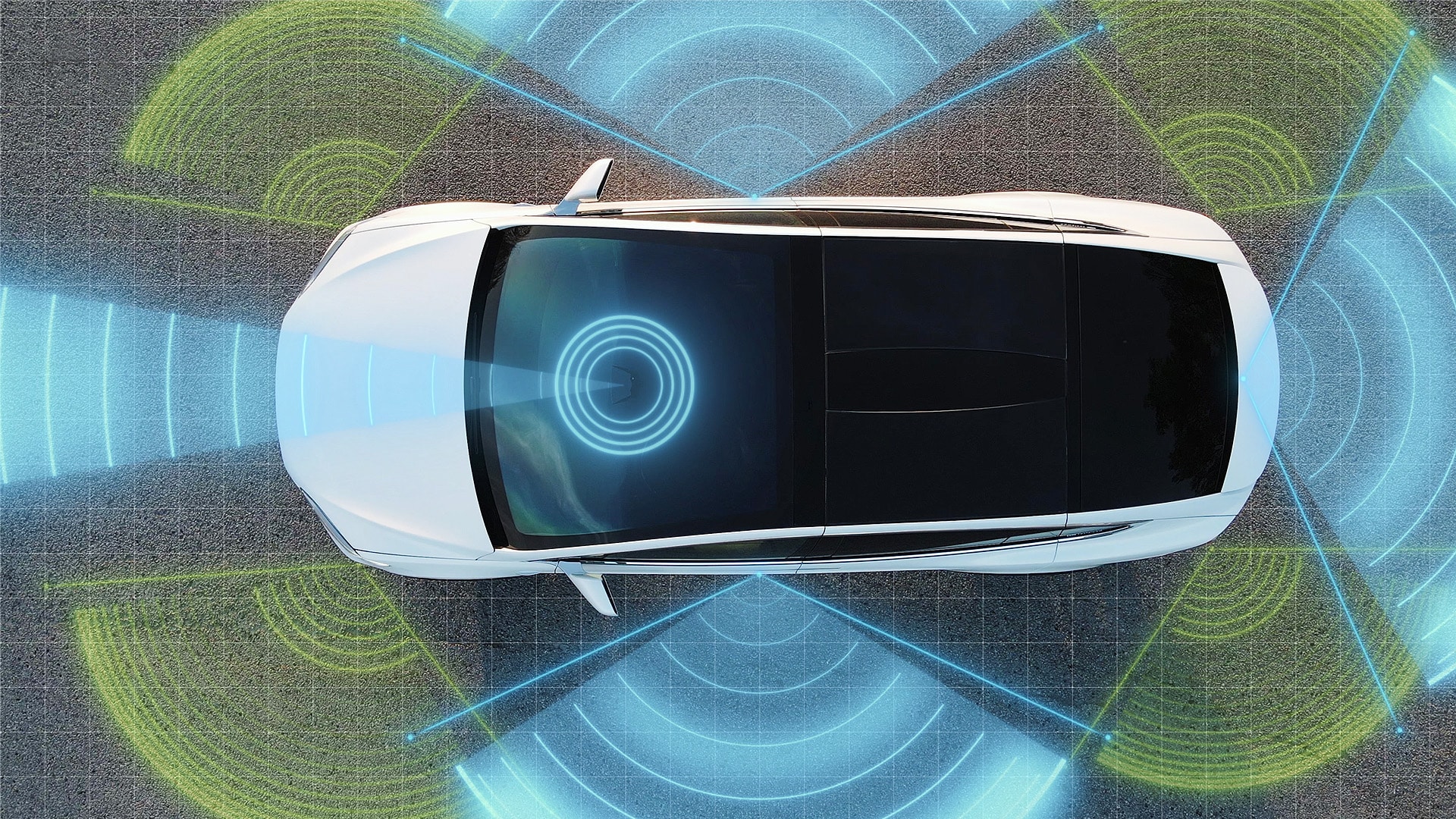
In the realm of autonomous vehicles (AVs), sensor technology plays a pivotal role in ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency. Two primary sensor types utilized are Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) and radar. Each offers unique capabilities and limitations that influence their application in AV systems. Understanding the distinctions between LIDAR and radar is essential for grasping their respective roles in autonomous driving technology.automotiveresearchnews.com
Understanding LIDAR Technology
LIDAR operates by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the pulses to bounce back from objects. This process enables the creation of high-resolution 3D maps of the vehicle’s surroundings. LIDAR’s precision allows for accurate detection of objects, lane markings, and other critical features essential for navigation.automotiveresearchnews.comTheTalka+2naamarket.net+2sapien.io+2
Advantages of LIDAR:

- High Resolution: LIDAR provides detailed 3D imaging, allowing for precise object detection and classification.
- Accurate Mapping: It creates accurate maps of the environment, aiding in localization and path planning.
- Effective in Low Light: LIDAR operates effectively in low-light conditions, enhancing nighttime driving capabilities.Oliver Wyman+7LTS GDS+7TheTalka+7sapien.io+1WIRED+1
Limitations of LIDAR:

- Cost: LIDAR systems are generally more expensive, which can increase the overall cost of AVs.
- Weather Sensitivity: Performance can degrade in adverse weather conditions such as heavy rain or fog.
- Limited Range: LIDAR typically has a shorter detection range compared to radar.onzuu.com+1sapien.io+1automotiveresearchnews.com+3naamarket.net+3onzuu.com+3
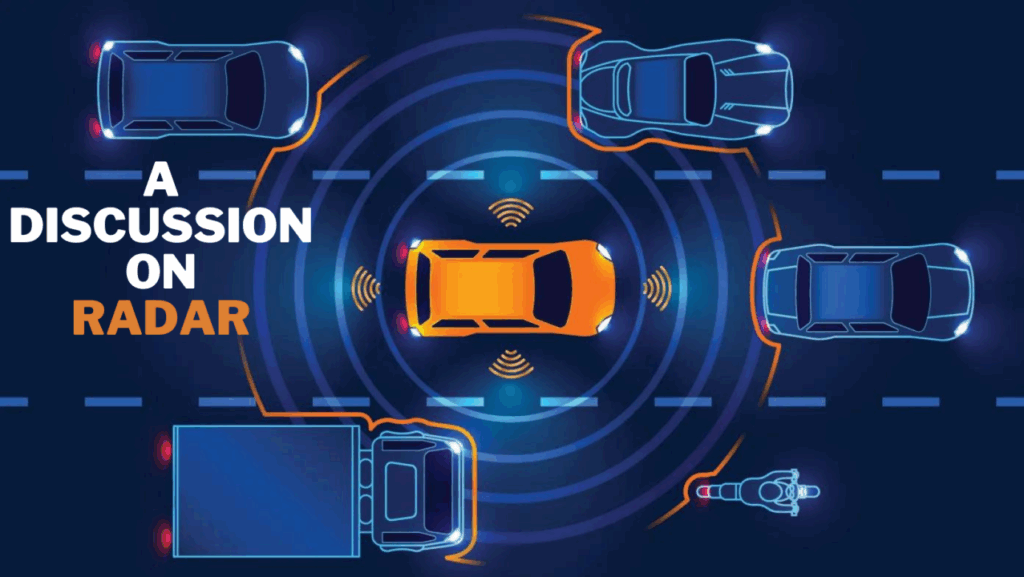
Exploring Radar Technology

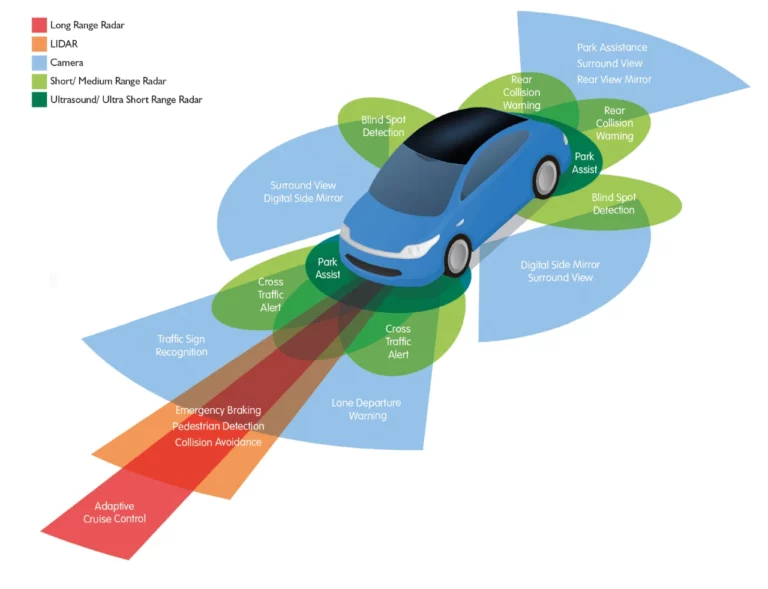
Radar utilizes radio waves to detect objects and measure their distance and speed. It is widely used in various applications, including automotive systems, due to its robustness and reliability.automotiveresearchnews.com+1onzuu.com+1
Advantages of Radar:
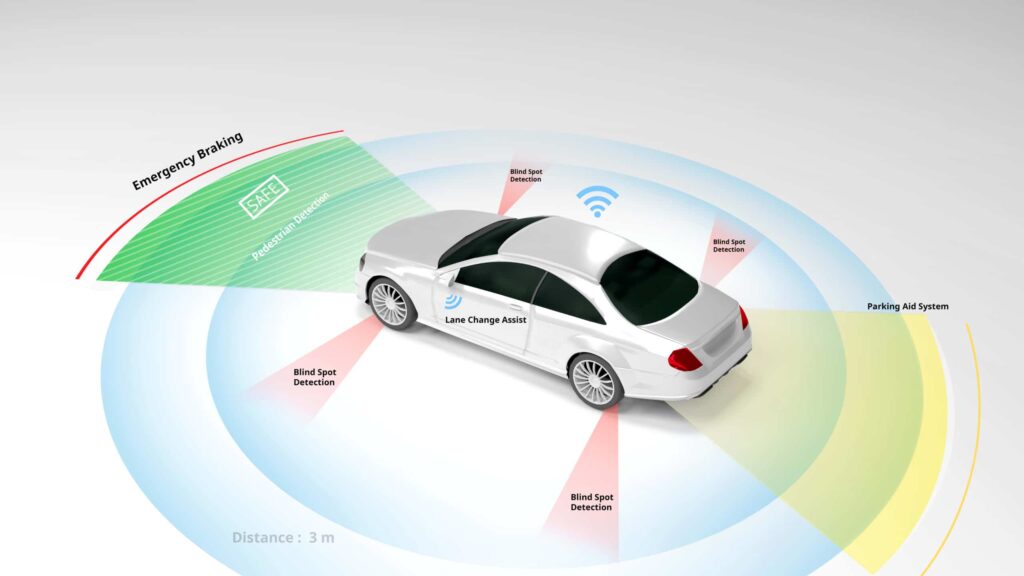
- All-Weather Capability: Radar performs reliably in adverse weather conditions, such as rain, fog, and snow.
- Long Range: It can detect objects at greater distances, making it suitable for highway driving.
- Cost-Effective: Radar systems are generally less expensive than LIDAR, making them more accessible for mass production.LTS GDS+4TheTalka+4dpvtransportation.com+4drive-electric+6automotiveresearchnews.com+6dpvtransportation.com+6naamarket.net+1automotiveresearchnews.com+1
Limitations of Radar:
- Lower Resolution: Radar provides less detailed imaging compared to LIDAR, which can affect object classification.
- Limited Object Recognition: It may struggle to distinguish between similar objects, such as a pedestrian and a cyclist.
- Susceptibility to Interference: Radar signals can be affected by interference from other radar systems.automotiveresearchnews.comdpvtransportation.com
Comparative Analysis: LIDAR vs. Radar
| Feature | LIDAR | Radar |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Laser pulses | Radio waves |
| Resolution | High | Moderate |
| Range | Moderate | Long |
| Weather Performance | Poor in adverse conditions | Excellent in all conditions |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Object Classification | Excellent | Fair |
Real-World Applications in Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles often integrate both LIDAR and radar to leverage the strengths of each technology. This combination enhances the vehicle’s ability to perceive its environment accurately and reliably.Houston Chronicle+3onzuu.com+3drive-electric+3
Example 1: Volvo and DHL’s Driverless Freight Trucks
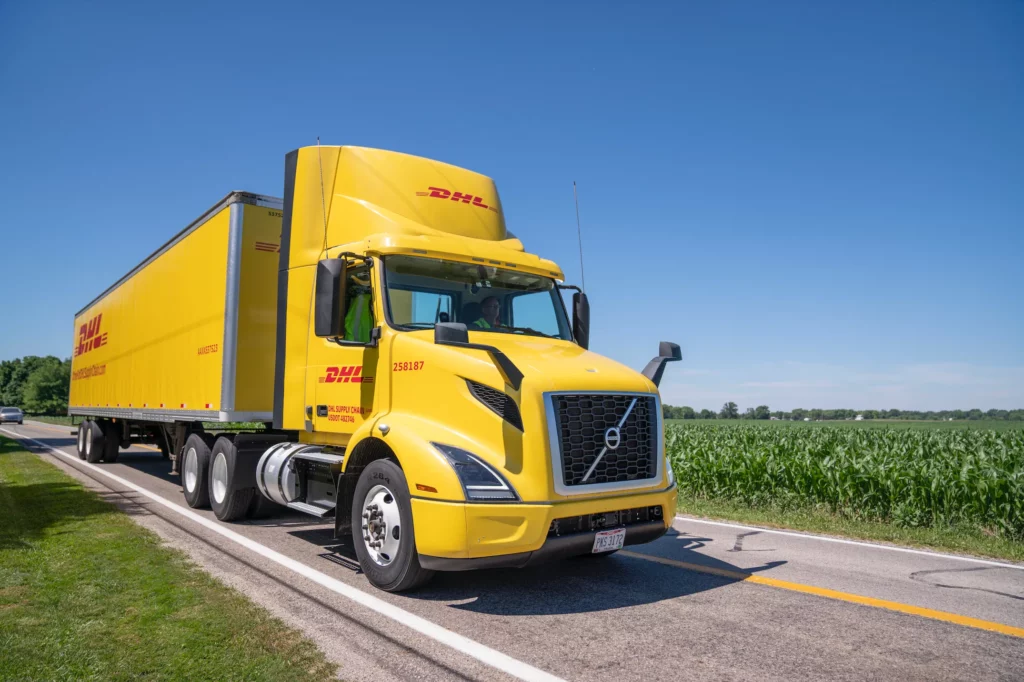

Volvo Autonomous Solutions and DHL Supply Chain have launched driverless freight trucks operating between Dallas and Houston. These trucks are equipped with long-range LIDAR and high-resolution cameras for nearly 360-degree obstacle detection. The integration of LIDAR allows for precise mapping and object detection, while radar ensures reliable performance in various weather conditions. Houston Chronicle
Example 2: BMW’s Autonomous Driving Tests
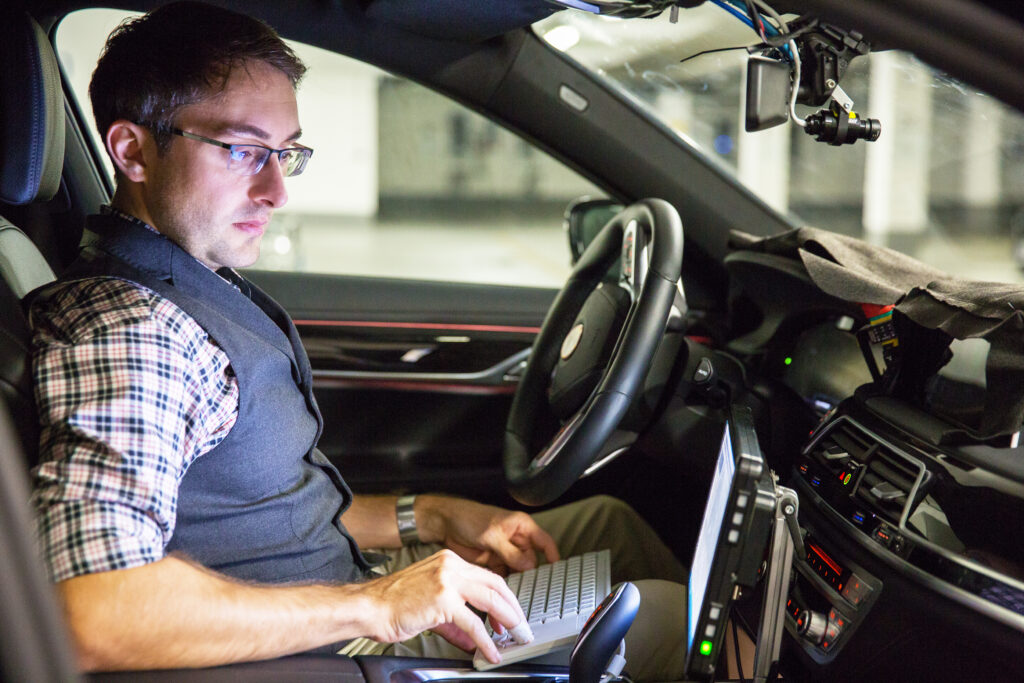

BMW has been testing semi-autonomous vehicles on the autobahn between Munich and Nuremberg. These vehicles utilize a combination of radar, LIDAR, ultrasound, video, and GPS to navigate safely. The integration of LIDAR provides detailed environmental mapping, while radar offers reliable performance in diverse driving conditions. WIRED
Example 3: Aurora’s Autonomous Freight Trucks
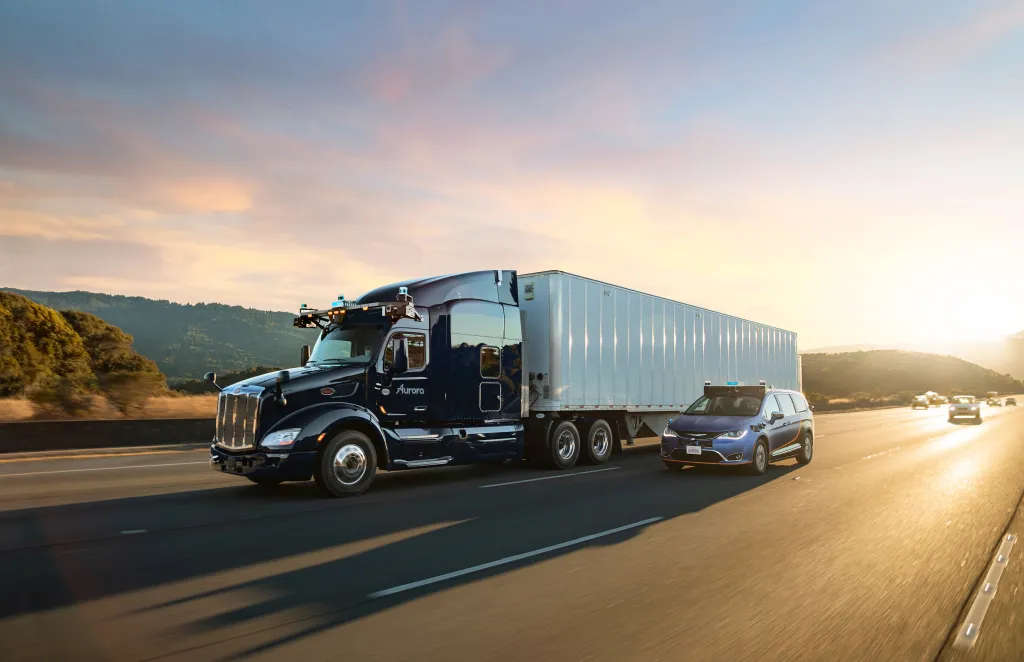

Aurora, in collaboration with Uber Freight, is developing autonomous freight trucks. These trucks are equipped with LIDAR and radar systems to ensure safe and efficient operation. The combination of LIDAR’s high-resolution mapping and radar’s all-weather capability enhances the vehicle’s perception system. Mindy Support+5Houston Chronicle+5Insights | Outsight+5onzuu.com
Benefits of Combining LIDAR and Radar
Integrating both LIDAR and radar technologies in autonomous vehicles offers several advantages:dpvtransportation.com
- Enhanced Perception: Combining the high-resolution mapping of LIDAR with the long-range detection of radar provides a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Improved Safety: The redundancy of using multiple sensor types reduces the likelihood of sensor failure, enhancing overall safety.
- Robust Performance: The complementary nature of LIDAR and radar ensures reliable operation in various environmental conditions.
Use Cases: Addressing Real-World Challenges
The integration of LIDAR and radar addresses several challenges in autonomous driving:
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Radar’s ability to perform in rain, fog, and snow ensures that autonomous vehicles can operate safely in diverse weather conditions.
- Nighttime Driving: LIDAR’s effectiveness in low-light conditions enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate at night.
- Complex Environments: The combination of LIDAR and radar allows for accurate mapping