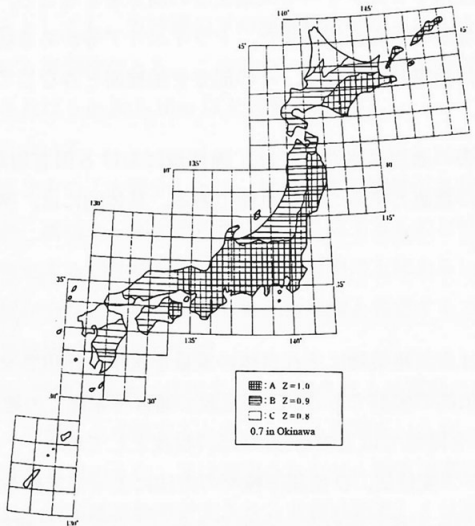
Japanese Earthquake Proof House Design
Designing an earthquake-proof house like those in Japan requires advanced engineering, smart materials, and seismic-resistant architecture. Japan is a global leader in earthquake-resilient construction due to its frequent seismic activity.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements behind Japanese earthquake-proof house design:
🏠 Japanese Earthquake-Proof House Design
🧱 1. Flexible Foundation Systems
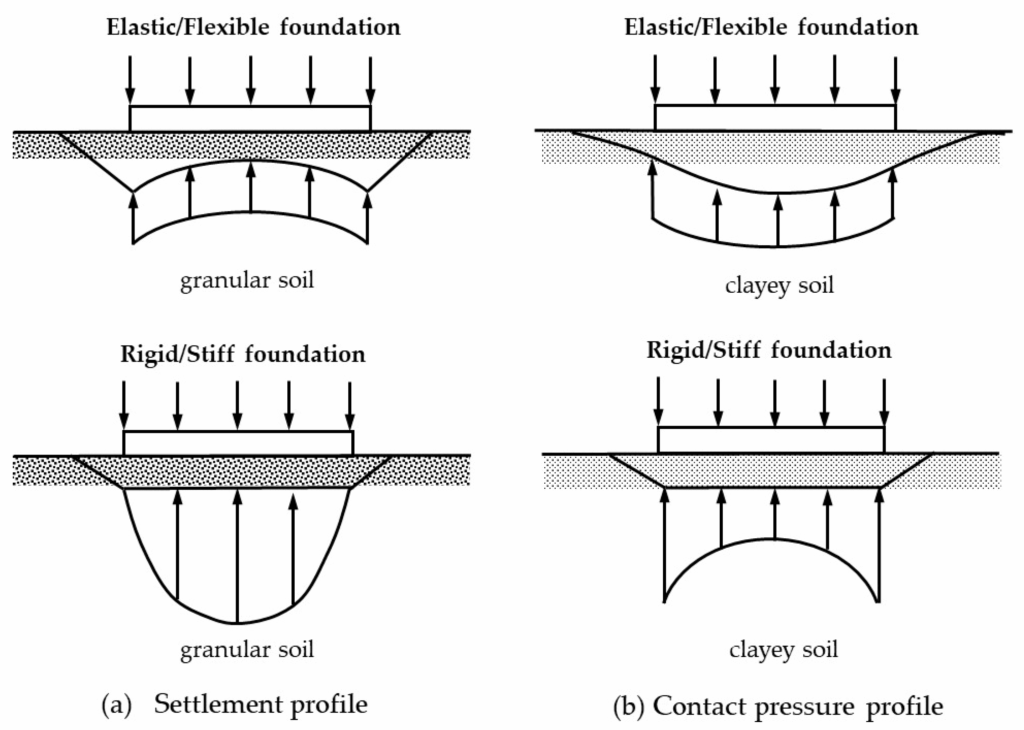
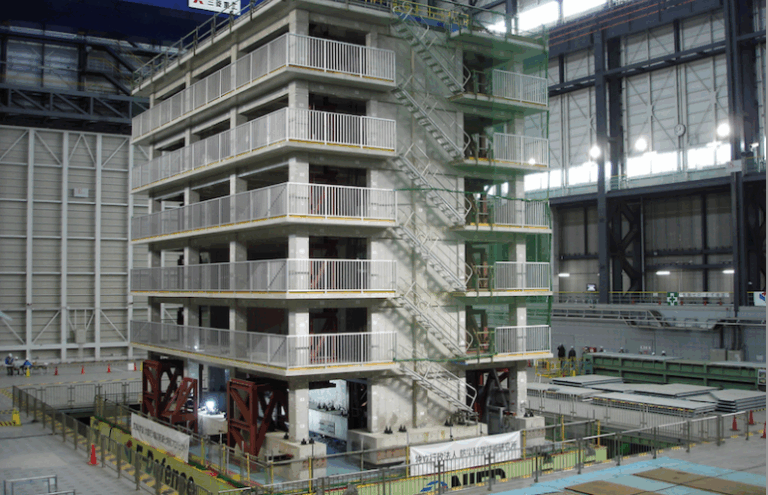
- Base Isolation (Seismic Isolation):
- The structure sits on rubber bearings or sliders that absorb seismic shocks.
- Reduces the transfer of ground movement to the building.
- Floating Foundation:
- Uses dampers or pads that allow the house to “float” slightly during quakes.
🔩 2. Structural Reinforcement

- Steel-reinforced concrete or cross-laminated timber (CLT) walls
- X-shaped bracing or shear walls to resist lateral forces
- Use of lightweight, high-tensile materials to reduce top-heaviness
🧬 3. Dampening Systems
- Tuned mass dampers (TMD): Heavy weights installed in the attic or roof that move opposite to seismic motion to counterbalance swaying.
- Viscous dampers (like automotive shock absorbers) reduce oscillation.
These systems are common in skyscrapers but scaled versions are now used in residential homes.
🧯 4. Smart Building Materials

- Shock-absorbing wood, traditional Japanese Hinoki or engineered timber
- Reinforced flexible joints to allow controlled movement
- Fire-retardant, crack-resistant walls and finishes
🏗️ Design Principles
1. Low Centre of Gravity
- Two-story max height
- Light roofs (e.g., metal or tile instead of concrete)
2. Symmetry and Simplicity

- Square or rectangular floor plans distribute force evenly
- Avoid cantilevered sections or overly complex designs
3. Separation Joints

- Small expansion joints between structures (e.g., garage and house) to prevent impact damage
4. Roof Design
- Lightweight roofing securely anchored
- Aerodynamic shape reduces uplift
💡 Modern Technologies Used in Japan
- Early warning systems integrated into smart homes (connects to national earthquake alert network)
- Self-healing materials (in experimental stage)
- Modular and prefab houses using quake-tested components
🧾 Building Codes & Standards
Japan’s Building Standard Law mandates:
- All buildings withstand Level 6 (severe) quakes
- Public buildings and infrastructure must survive Level 7 (catastrophic)
Designs follow standards like:
- JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards)
- Building Seismic Safety Promotion Act
🛖 Traditional Japanese Techniques That Still Work
- Tatami mats: flexible flooring that absorbs shock
- Shoji screens: lightweight, won’t cause harm if dislodged
- Wooden post-and-beam (kanawa tsugi) joinery: naturally absorbs motion
✅ Summary: Earthquake-Proof Design Checklist
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Base isolation | Absorbs ground movement |
| Shear walls / X-bracing | Provides lateral stability |
| Lightweight structure | Reduces toppling and inertia |
| Smart materials | Flex, absorb shocks |
| Simple layout | Even force distribution |
| Roof anchoring | Prevents detachment |
| Emergency systems | Ensures post-quake safety |