How To Build Earthquake Safe Home
Building an earthquake-safe home involves careful planning, smart material choices, and structural engineering techniques designed to withstand seismic forces. While no building is truly “earthquake-proof,” you can make your home earthquake-resistant.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to building an earthquake-safe home:
🛠️ Step-by-Step: How to Build an Earthquake-Safe Home

🧭 1. Site Selection and Soil Testing
- Avoid steep slopes, landfill areas, or soft clay soil — they amplify seismic motion.
- Get a geotechnical soil report to assess site stability.
- Prefer bedrock or compacted soil for the foundation.
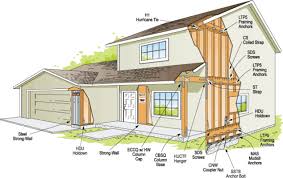
🧱 2. Foundation Design
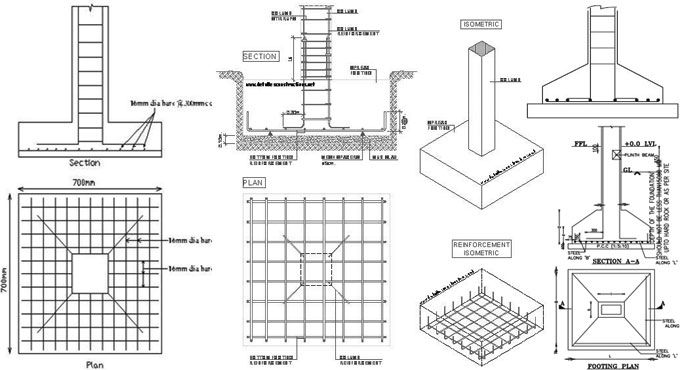
A strong foundation anchors the structure and absorbs seismic energy.
- Use a reinforced concrete slab or deep footings
- For high-risk areas, consider:
- Base isolation systems (rubber bearings, sliders)
- Pile foundations on soft soils
- Anchor the house securely to the foundation with bolts or straps
🏗️ 3. Structural Framing
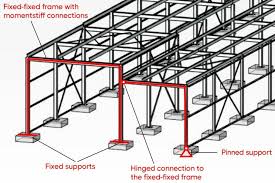
Use strong, flexible materials that move without breaking:
Wood Frame (Timber)
- Lightweight and flexible — ideal for seismic areas
- Use engineered wood or cross-laminated timber (CLT) for added strength
Steel Frame
- Excellent for lateral (side-to-side) movement resistance
- Often used in combination with concrete or wood
Reinforced Concrete
- High strength, especially when combined with rebar (steel)
- Add shear walls and moment-resisting frames
📏 4. Shape & Symmetry
- Keep the floor plan compact, symmetrical, and simple
- Avoid:
- Large cantilevers
- Split-levels without reinforcement
- Heavy roofs or irregular layouts
A balanced design prevents torsional stress (twisting) during quakes.
🪜 5. Wall and Roof Reinforcement
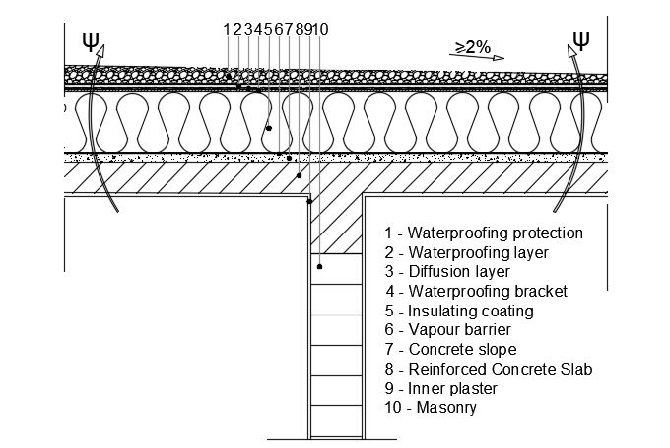
- Shear walls resist lateral forces; place on all sides
- Use metal connectors, tie-downs, and brackets at joints
- Secure the roof to the walls using hurricane or seismic clips
- Keep roof materials light (e.g., metal or fiber cement)
🚪 6. Windows, Doors, and Openings
- Minimize large openings on load-bearing walls
- Use tempered or laminated glass for windows
- Reinforce door and window frames with steel or engineered wood
🪛 7. Interior Safety Features

- Bolt or brace:
- Tall furniture
- Water heaters
- Appliances
- Use flexible connectors for gas lines and plumbing
- Install automatic gas shutoff valves
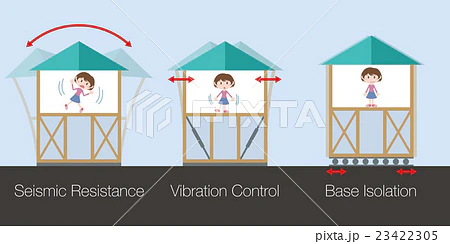
⚙️ 8. Optional: Advanced Seismic Tech
- Base isolators: Absorb seismic waves before they reach the home
- Dampers: Reduce building swaying (used in tall structures)
- Smart sensors: Monitor seismic stress in real time
🏗️ 9. Follow Seismic Building Codes

- Comply with local codes (e.g., California Building Code, Japan’s BSL, or NZ Standards)
- Hire a licensed structural engineer to design and approve plans
- Use certified builders experienced in seismic construction
✅ Earthquake-Safe Home Checklist
| Feature | Recommended? |
|---|---|
| Soil testing | ✅ |
| Reinforced foundation | ✅ |
| Shear walls | ✅ |
| Roof anchoring | ✅ |
| Symmetrical floor plan | ✅ |
| Flexible materials (wood/steel) | ✅ |
| Secured gas and utilities | ✅ |
| Professional structural engineer | ✅ |
📘 Bonus: Design Tips from Japan & California
- Raised, lightweight homes with low center of gravity
- Use tatami or wood floors that absorb shock
- Floating foundations on rubber pads for luxury builds
- Avoid heavy roof tiles or unreinforced chimneys