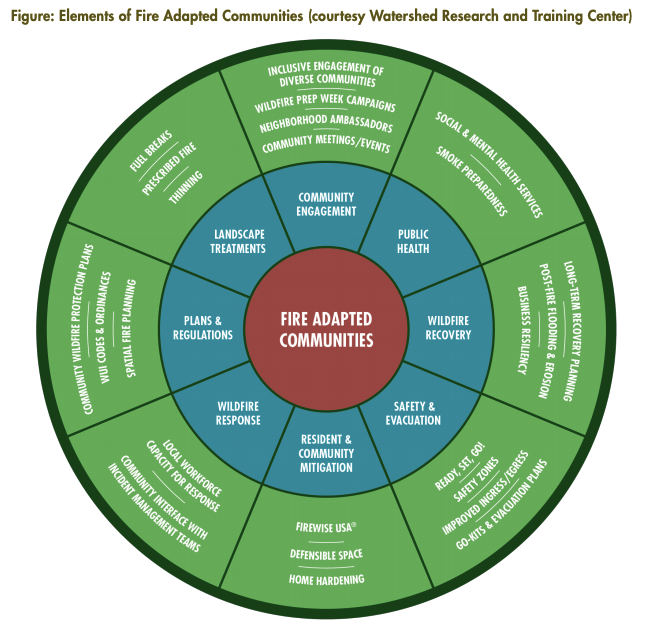
Wildfire Prevention Strategies California

California, due to its dry climate, wind patterns, and expanding wildland-urban interface, faces extreme wildfire risks. As a result, wildfire prevention strategies are multi-layered and involve government agencies, utilities, communities, and individual property owners.
Here’s a detailed overview of wildfire prevention strategies in California:
🔥 1. Vegetation Management (Fuel Reduction)

A. Prescribed Burns
- Controlled fires set intentionally to reduce underbrush and dead vegetation.
- Managed by CAL FIRE and local fire agencies.
- Helps mimic natural fire cycles and prevent mega-fires.
B. Mechanical Thinning
- Use of chainsaws, masticators, or heavy machinery to clear brush and small trees.
- Often used where burns are unsafe.
C. Grazing
- Targeted goat or sheep grazing to reduce grass and light brush in fire-prone areas.
🏡 2. Defensible Space Regulations
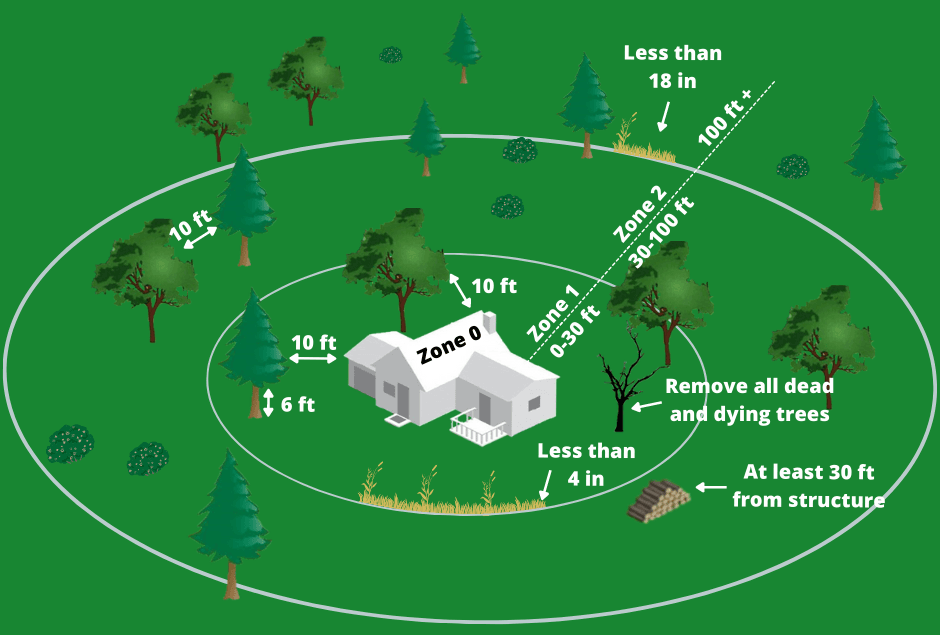
California law (Public Resources Code 4291) requires homeowners in wildfire-prone areas to maintain:
- Zone 1 (0–5 ft from structures): Remove anything flammable — vegetation, mulch, wood piles.
- Zone 2 (5–100 ft): Thin trees, prune branches, reduce fuel ladders.
- Tree spacing and vertical clearance: Must separate tree crowns and clear branches above rooflines.
🏘️ 3. Fire-Resistant Building Codes
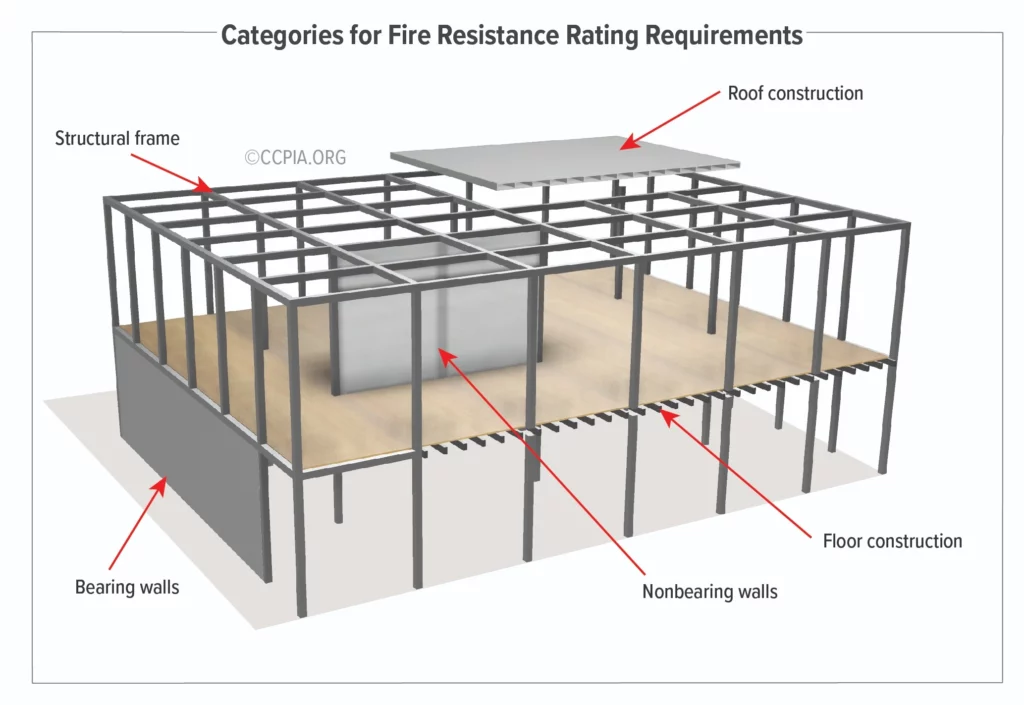
A. Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) Code (Chapter 7A of California Building Code)
- Applies to new construction in fire hazard zones.
- Requires:
- Non-combustible roofing and siding materials (e.g., metal, stucco, fiber cement).
- Ember-resistant vents and soffits.
- Dual-pane tempered glass windows.
B. Retrofit Incentives
- State and local programs help homeowners upgrade older homes to be more fire-resilient.
🌲 4. Utility Safety Programs

A. Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS)
- Power lines are shut off during extreme fire risk conditions to prevent sparks.
B. Grid Hardening
- Utilities like PG&E and SCE are:
- Undergrounding power lines
- Installing covered conductors
- Adding remote monitoring systems
C. Vegetation Clearing Around Power Lines
- Strict right-of-way clearing to reduce ignition risk.
🚒 5. Community and Statewide Programs

A. Firewise USA® Program
- Encourages neighborhoods to develop local fire safety plans and maintain defensible space.
B. CAL FIRE’s Fire Prevention Grants
- Funding for local agencies, nonprofits, and tribes to do vegetation management, education, and planning.
C. Ready, Set, Go! Program
- Public education campaign on wildfire preparedness and evacuation.
🛰️ 6. Technology and Early Detection

- Wildfire cameras (AlertCalifornia network)
- AI wildfire detection using satellite and sensor data
- Drones used by CAL FIRE to map fires and identify hotspots
🧑⚖️ 7. Land Use Planning and Zoning
- Restricting or guiding development in fire hazard severity zones (FHSZ).
- Requiring wildfire risk assessments before development approvals.
- Promoting clustered development over sprawl.
✅ Summary Table
| Strategy | Main Goal |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burns | Reduce fuel loads |
| Defensible Space | Protect structures |
| Fire-Resistant Construction | Withstand ember attack |
| PSPS & Grid Hardening | Prevent utility-sparked fires |
| Community Programs | Localize prevention efforts |
| Detection Technology | Rapid response |
| Zoning Laws | Avoid building in high-risk areas |