Green Roof Construction
Green roof construction—also called a living roof—involves layering vegetation, growing medium (soil), and waterproofing materials on top of a traditional roof structure. These eco-friendly systems offer insulation, stormwater management, and aesthetic benefits, making them a popular feature in sustainable architecture.
🌿 What Is a Green Roof?
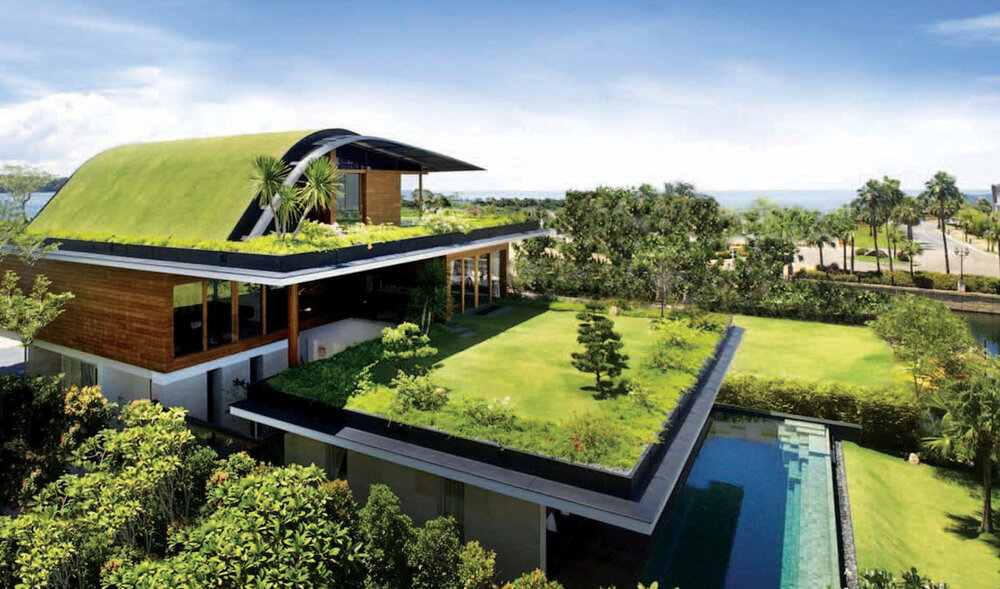

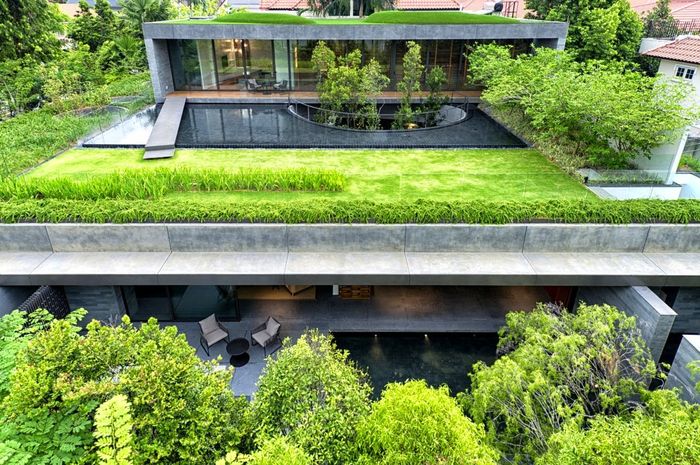
A green roof is a roofing system that supports plant growth over a waterproof membrane. It’s used on both residential and commercial buildings to reduce heat absorption, manage runoff, and increase biodiversity.
🧱 Layers of a Green Roof (Typical Structure)
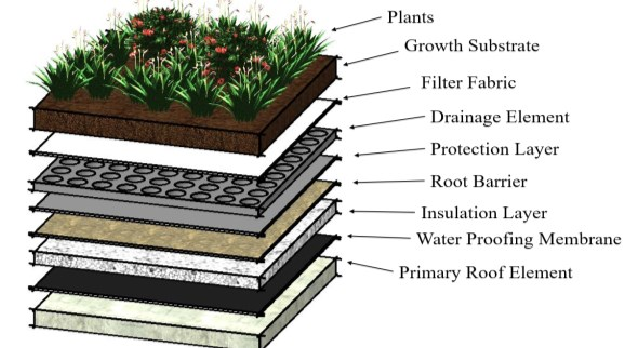
- Structural Roof Deck
- Must be strong enough to support the added weight.
- Materials: Concrete, metal, or wood (depending on load capacity).
- Vapor Control Layer(optional, climate-dependent)
- Prevents moisture migration from inside the building.
- Thermal Insulation
- Improves energy efficiency and interior comfort.
- Waterproofing Membrane
- Essential for protecting the building from leaks.
- Must be root-resistant to prevent damage from plant roots.
- Root Barrier
- Protects waterproof layer from root intrusion.
- Drainage Layer
- Allows excess water to escape.
- Often includes a filter to prevent soil clogging.
- Filter Fabric
- Prevents soil from washing into the drainage layer.
- Growing Medium (Soil Substrate)
- Lightweight engineered soil mix tailored for plant health and water retention.
- Vegetation Layer
- Chosen based on climate, roof pitch, and intended use.
- Common plants: Sedum, grasses, herbs, wildflowers.
🌱 Types of Green Roofs
| Type | Description | Plant Types | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extensive | Shallow (2–6 inches soil), light weight | Sedum, moss, small grasses | Low |
| Intensive | Deep soil (6+ inches), supports trees and shrubs | Turf, flowers, shrubs, small trees | High |
| Semi-Intensive | Mix of both | Grasses, herbs, flowers | Moderate |
🛠️ Key Considerations for Construction
- Structural Load: Ensure the building can bear additional weight (from soil, water, and vegetation).
- Waterproofing: Use high-quality, root-resistant membranes (e.g., EPDM, PVC).
- Drainage: Prevents water pooling and structural damage.
- Plant Selection: Choose drought-tolerant, low-maintenance species unless irrigation is planned.
- Slope: Green roofs can be installed on flat or sloped roofs (generally up to 30° with special reinforcement).
- Access & Maintenance: Plan for accessibility if regular upkeep is needed (especially for intensive systems).
✅ Benefits of Green Roofs
- 🌡 Thermal insulation → Reduces heating and cooling costs
- 🌧 Stormwater management → Absorbs rainwater, reducing runoff
- 🌬 Air quality improvement → Filters pollutants
- 🌻 Urban biodiversity → Creates habitats for insects, birds
- 🏙 Aesthetic & property value → Attractive feature that can increase resale value
🧰 Common Products & Materials
| Component | Recommended Options |
|---|---|
| Waterproof Membrane | Sika Sarnafil, Firestone EPDM |
| Drainage Layer | Optigreen, ZinCo, EnkaDrain |
| Growing Medium | Rooflite, Skyland USA |
| Vegetation | Sedum mats, wildflower seed mixes |






